


At EXWHYZEE Technologies Ltd, our mission is to empower individuals, businesses, and government entities through innovative IT solutions. Since our inception, we have been at the forefront of designing cutting-edge technologies to cater to diverse needs.
I am thrilled to share an exciting new initiative - the EXWHYZEE Digital Skills Training Program. Funded by the IGF Innovation Grant, we will train 1000 youths in Abia State on a range of digital skills, equipping them with the knowledge and tools to thrive in the evolving job market.
Our experienced team is dedicated to bridging the classroom-industry gap, ensuring participants gain practical, hands-on experience in the latest technologies.
To digitally automate every business in Nigeria and its surrounding regions, leveraging cutting-edge technology
We intend to develop the right human resources and software for every business using all industrial standards.
Our core value is to make life easy through technology, we trive to grow your business and impact positively to the society
At EXWHYZEE, our objective is to deliver tailored design solutions that align with our clients' business objectives.
We make serious research on all our projects ranging from getting the necessary information.
Our project development teams now takes this next step in turning the information gathered to a tangible solution
After development, our team of software tester ensures that the solution is functional and can serve the purpose it was created.
The project now been developed is handed to our esteemed clients as a final solution/product.
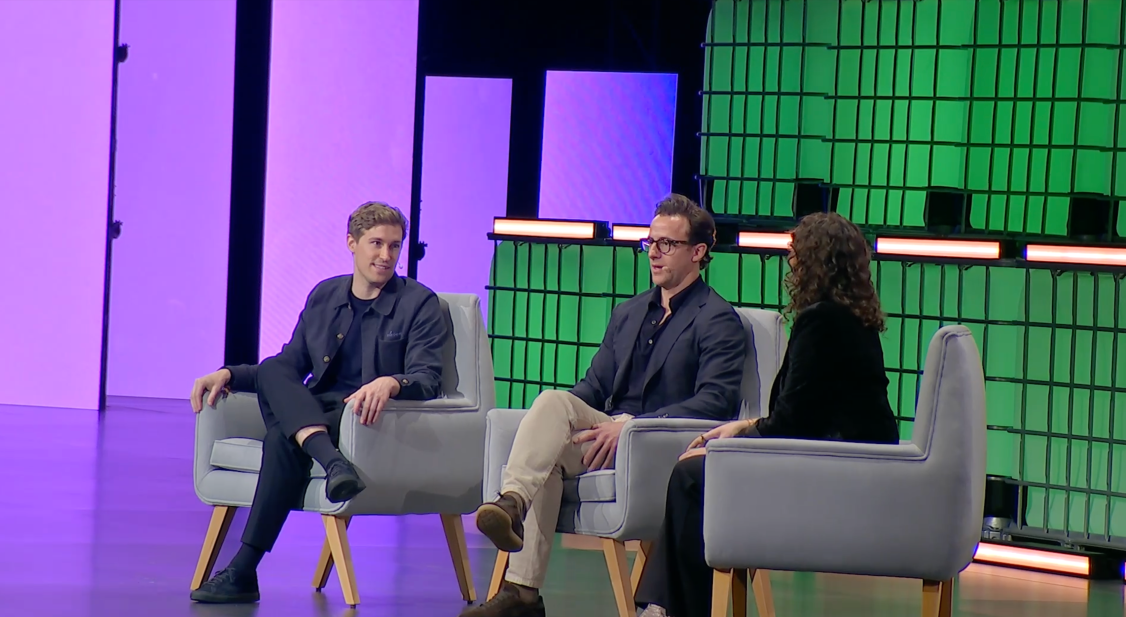





ElevenLabs co-founder and CEO Mati Staniszewski believes voice is emerging as the next primary interface for AI, shaping how people will increasingly engage with machines as AI systems move beyond text-based and screen-driven interactions.

Meta has confirmed that it is currently testing Vibes as a standalone application. Originally launched last September, Vibes enables users to create and share short AI-generated videos, as well as browse a dedicated feed showcasing AI-created content from other users.
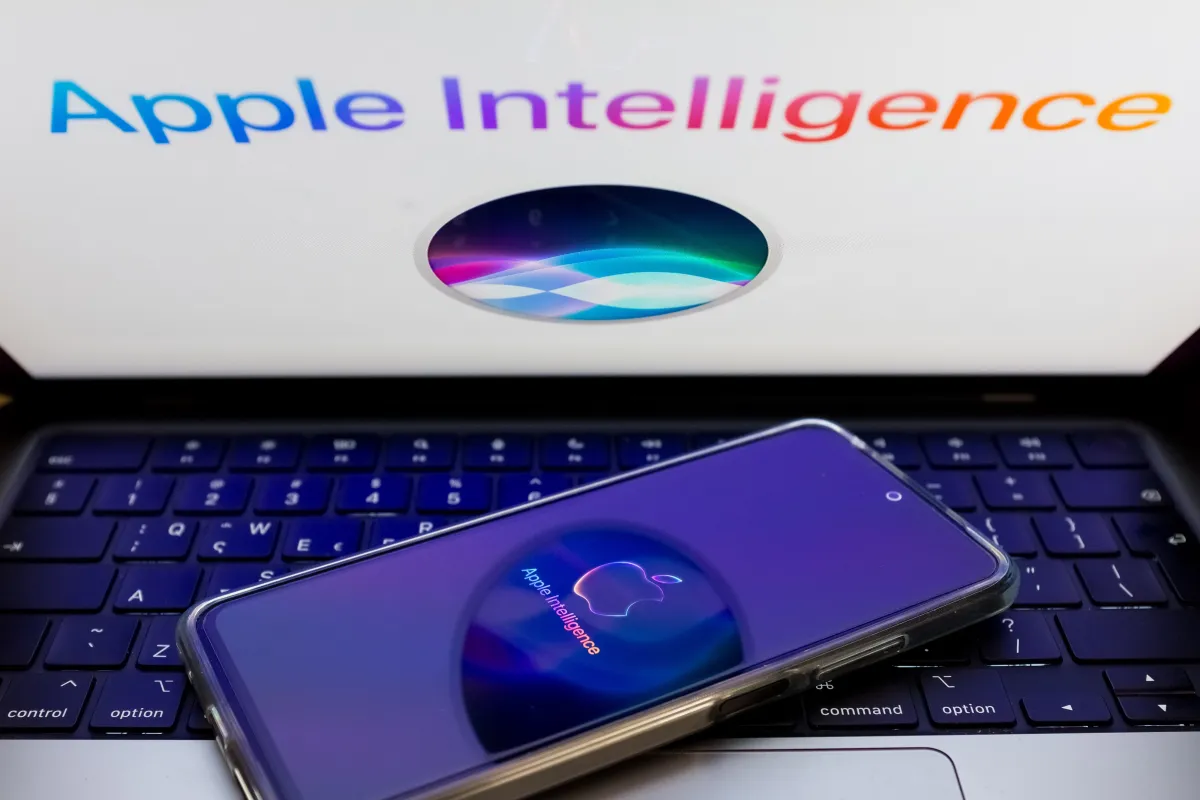

According to Bloomberg’s Mark Gurman, Apple’s long-anticipated overhaul of Siri may transform the assistant into a ChatGPT-style chatbot, with the revamped feature expected to be integrated into iOS 27 and highlighted at Apple’s WWDC in June.
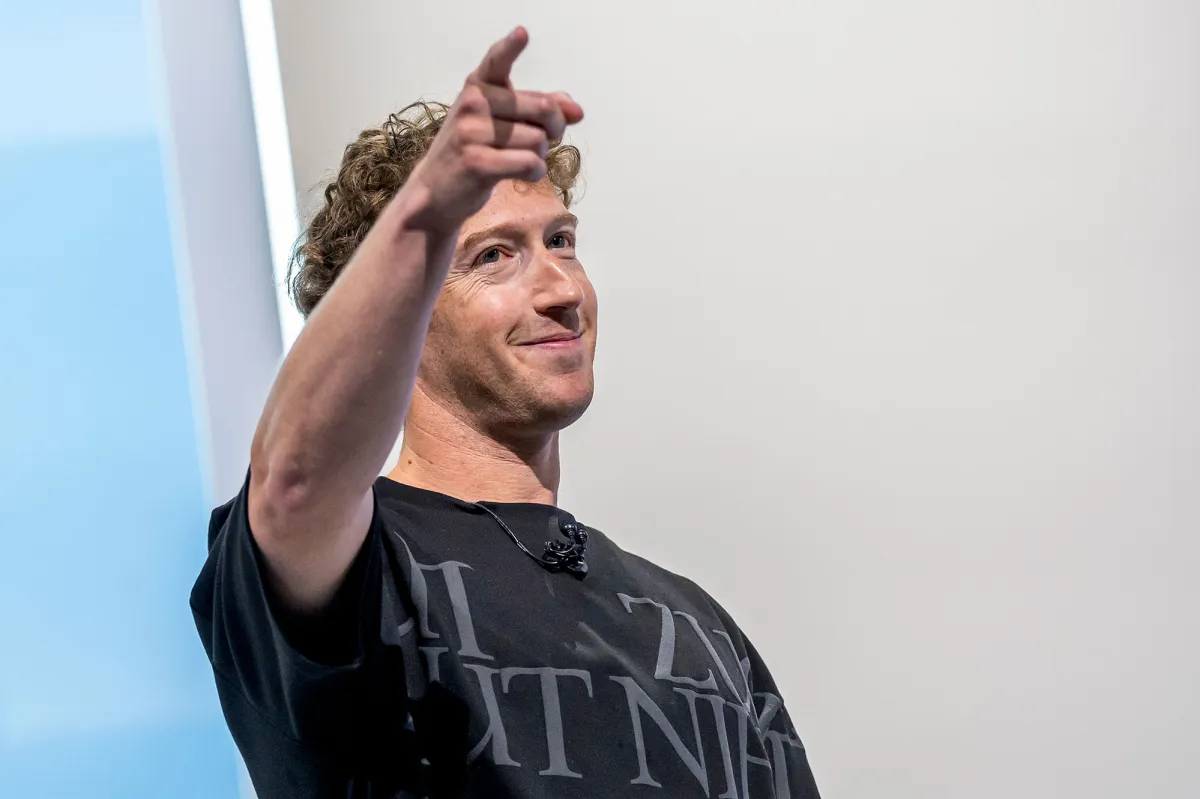

Last year, Meta outlined ambitious capital expenditure plans, signaling significant investment in building capacity for its AI operations.
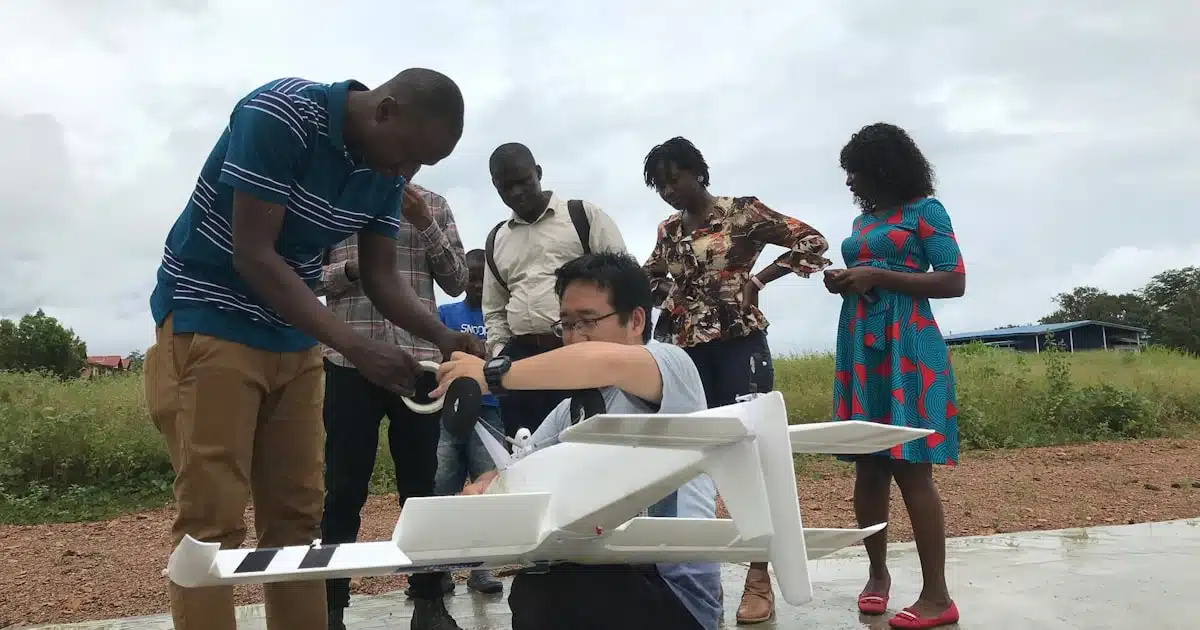

Sora Technology, which leverages drones and artificial intelligence to combat infectious diseases, has secured a further $2.5 million in a second close of its late seed round to expand its malaria elimination initiatives across Africa.

Flutterwave has finalized a multi-million-dollar acquisition of Mono, a Nigerian open-banking company.
An increasing number of web browsers are beginning to test agent-based features designed to perform tasks on users’ behalf, such as purchasing items or booking tickets. While these capabilities offer convenience, they also introduce potential security concerns that could result in financial loss or data exposure.
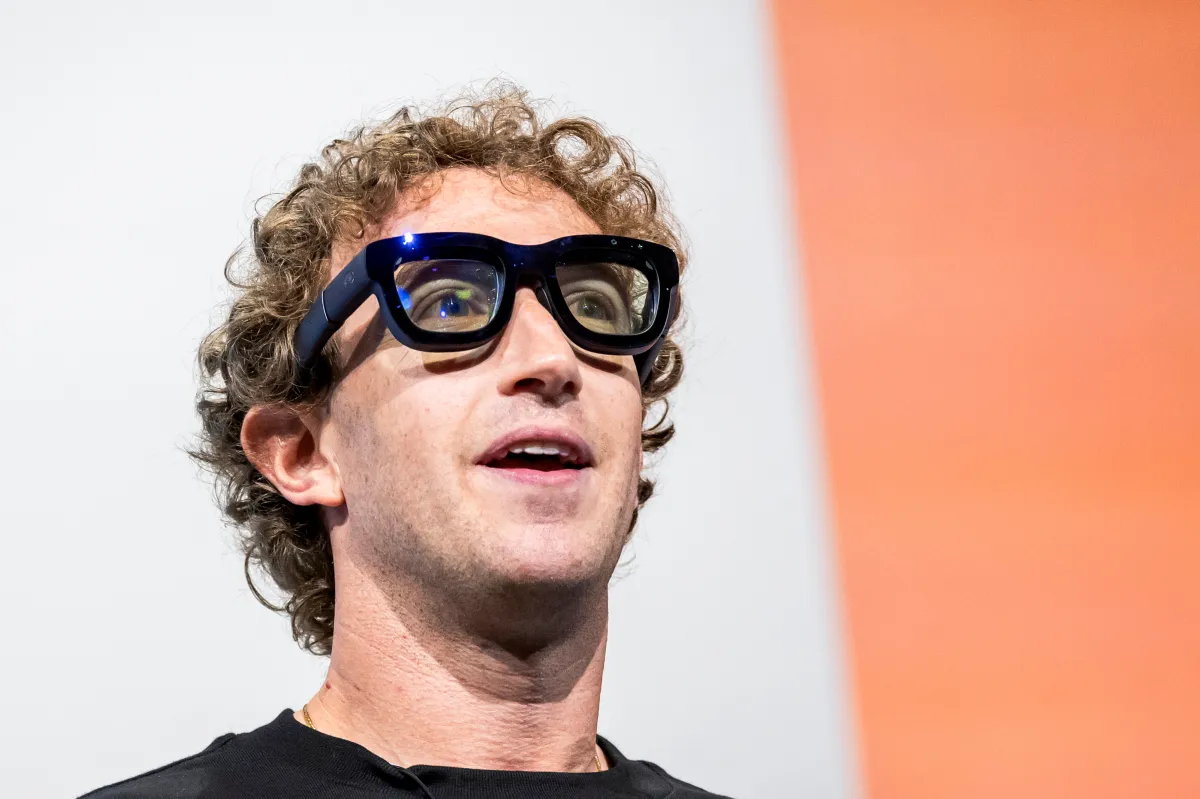

Amid an unprecedented wave of AI development, Meta is outspending most of its competitors. The company is currently constructing two massive data centers, and reports suggest that U.S. infrastructure investments could reach as high as $600 billion over the next three years.

X is rolling out a new marketplace that lets Premium subscribers request and purchase inactive usernames. The platform will include both free and paid options for acquiring available handles, with rare ones priced anywhere from $2,500 to several million dollars, according to X.

OpenAI unveiled its new Atlas web browser during an unexpected livestream event, which began with CEO Sam Altman addressing the audience directly.